Sie haben sich erfolgreich abgemeldet.
Noch nicht registriert?
Alternative to antibiotics in wound care
Infected wounds
A common complication of wounds (and chronic wounds in particular) are infections. Wound infections compromise the normal healing process and may lead to a reduction in the patients’ quality of life. Even worse, they bear the risk of amputation and lethal sepsis. Additionally, as if losing a limb or a patient's life is not enough, wound infections provide a great burden to the health care system.
That is why it is important to find the best strategy to prevent, diagnose and manage wound infections.
-
Up to
0%
of chronic wounds contain biofilm with a role in wound infection.(1)
-
0%
of chronic wounds are estimated to be infected.(2)
Chronic wounds
Prevention and treatment of wound infection
The wound infection continuum(3) describes the different stages of how microbes impact a wound and consequently shows when antimicrobials are indicated and when not. This helps wound care practitioners to find the best strategy to prevent, diagnose and manage wound infection. Get to know our unique therapy concept that covers all stages of the wound infection continuum: Prontosan® to prevent the formation of biofilm and to decrease the bacterial burden,(4) and Askina® Calgitrol®, a range of primary wound dressings consisting of a silver alginate matrix, which provides antimicrobial barrier and helps prevent contamination from external bacteria.
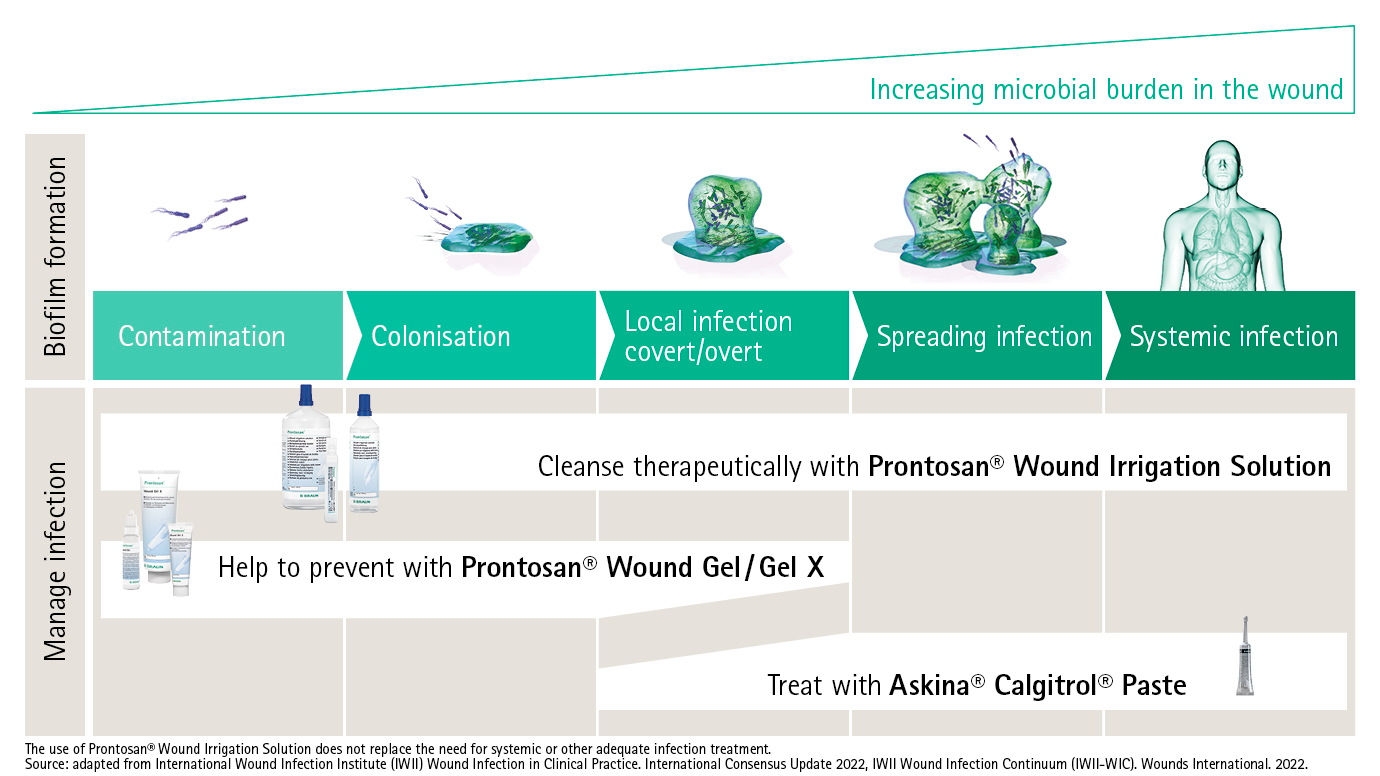
Early Intervention strategies for wound infection management
A thorough wound assessment is essential for preventing and treating wound infections and all types of complications that can accompany them. During our B. Braun symposium, we focused on the importance of recognizing the signs of a developing wound infection and how to assess them using the Wound Infection Continuum.
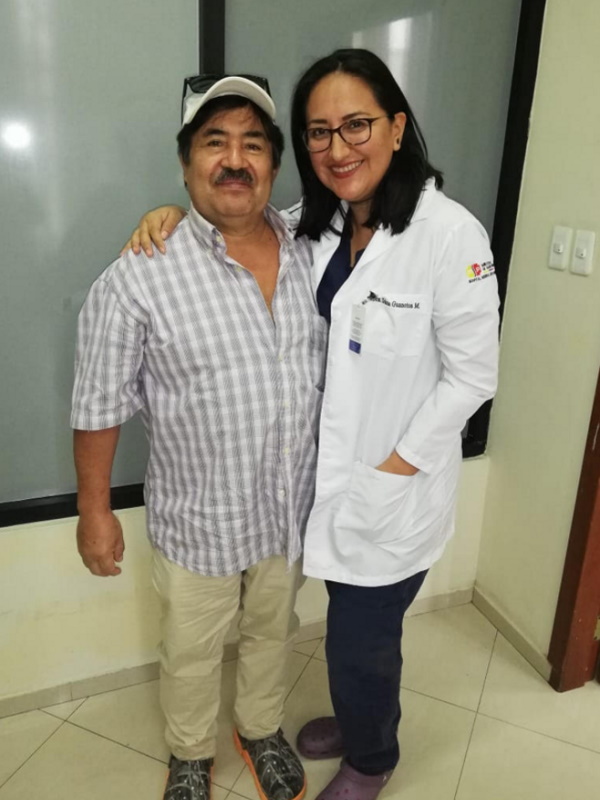
We showed how proper diagnosis and product selection strategies can help you prevent and treat wound infections. Prontosan® and Askina® Calgitrol® make a perfect match in the combat against wound infections. This effective combination has also restored health to the patient Miguel whose clinical case history was presented during the symposium to provide additional practical insights.
Your choice matters – how would you have treated Miguel’s wound? We invite you to watch our symposium video hereunder.
An independent case series(5)
Case report: The use of Prontosan® in combination with Askina® Calgitrol®
The following case studies were carried out to evaluate the efficacy of a biofilm remover/cleanser in gel form - Prontosan® together with the use of an ionic releasing silver alginate - Askina® Calgitrol® Paste or Askina® Calgitrol® Thin - when used on infected wounds.
Treatment protocol
- The following treatment protocol was followed for all wounds in the study:
- Wounds were soaked for 15–20 minutes with Prontosan® gel or Prontosan® irrigation solution moistened gauze. Both the gel and the soaked gauze was kept in place by using cling film, gel was wiped away with saline gauze and soaked Prontosan gauze was used to wipe the wound
After wound cleansing, Calgitrol® Thin or Calgitrol® paste was applied depending on wound size and depth - The secondary dressing applied varied from non-adhesive foam to high-absorbent composite dressing depending on exudate levels
Results: Infection resolve time
All wounds showed a significant reduction in terms of clinical signs of infection within the first week of treatment. Some 50% of all wound infections were completely resolved by week 2. Eighty-one per cent of all wounds had no clinical signs of infection in less than 3 weeks. None of the patients were given any oral orintravenous antibiotics while on the study; all patients were only treated by using local antimicrobials. There was also a decrease in odour in all wounds.
Read the complete case reportWound infections are caused by the deposit and profileration of microorganisms in the surgical site of a susceptible host. There are numerous ways microorganisms can enter the wound bed. The infection can result in sepsis when bacteria spreads into the blood stream. If not actively treated, a sepsis can progress to multi-organ failures with a potentially lethal outcome.
The main objective is to prevent infections rather than to treat them.
In contact with wound exudate, the silver alginate matrix of Askina® Calgitrol® forms a soft gel. This helps both maintain a moist wound environment conducive to natural healing conditions as well as prevent contamination from external bacteria.

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) develops when microbes adapt and build immunity against antimicrobial drugs such as antibiotics. Over- and misuse of antibiotics increase this problem and present a serious health threat, since infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria are associated with longer hospital stays and higher death rates. Antimicrobial resistant infections currently cause at least 50,000 deaths across Europe each year.(6) And estimates are that by 2050 antimicrobial resistance will account for 10 million deaths worldwide per year, leading to annual global costs of US$100 trillion.(6)

AMR is a worldwide problem involving multiple sectors that is being addressed from different angles. The key strategy of this battle against the rise of antimicrobial resistance and healthcare-associated preventable infections is the adoption of local and national antimicrobial stewardship programs facilitating more prudent prescribing of antibiotics.

Regarding wound management, it is the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) which has taken the lead in introducing a tailored stewardship concept to wound care practitioners. The aim of this Antimicrobial Stewardship program is to reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics in wound care by promoting the use of non-antibiotic antimicrobials across all healthcare settings.(7)
1) Davis SC, Harding A, Gil J, Parajon F, Valdes J, Solis M & Higa A “Effectiveness of a polyhexanide irrigation solution on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in a porcine wound model” in International Wound Journal ISSN 1742-4801, 2017, 1-8, © 2017 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd doi: 10.1111/iwj.12734.
2) C. Dowsett: Adopting the two-week challenge in practice: making the case for silver dressings, Wounds UK, Vol. 10, N°2, 2014.1) International Wound Infection Institute (IWII). Wound infection in clinical practice. Wounds International 2016. https://www.woundinfection-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/IWII-Wound-infection-in-clinical-practice.pdf
3) International Wound Infection Institute (IWII). Wound infection in clinical practice. Wounds International 2016. https://www.woundinfection-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/IWII-Wound-infection-in-clinical-practice.pdf
4) To, E The effectivness of PHMB agents for the treatment of chronic wounds: A systematic review, Advance wound healing, 2016.
5) Naude L. The use of Prontosan® in combination of Askina® Calgitrol®: an independent case series. Wounds International, 2018 ; 9(1): 44-48. Available at (accessed 16.03.2018).
6) Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. Review on AMR, Wellcome Trust, HM Government, 2014. Available at: http://bit.ly/1VOck4o (accessed 31.03.2017)
7) https://ewma.org/what-we-do/antimicrobial-stewardship/
Stay connected with My B. Braun
With your personalized account, your online experience will be easier, more comfortable and safe.





